Researchers at Caltech have studied how the brain processes reward and risk, revealing the neural mechanisms behind decision-making. The findings shed light on the two-step process of reward and risk prediction errors in the brain, providing insights into understanding and potentially addressing psychiatric disorders.
Understanding the Brain's Decision-Making Process
When it comes to decision-making, our brains go through a complex process of weighing potential rewards and risks. Researchers at Caltech have been studying how the brain processes reward and risk, shedding light on the neural mechanisms behind our choices.
Meet Jessica Williams, an experienced content writer and blogger who combines her expertise in neuroscience with her passion for storytelling. With a background in psychology and neuroscience research, Jessica brings a unique perspective to understanding the brain's decision-making process.
In this article, we will explore how the brain calculates reward and risk based on past experiences. We'll delve into the two-step process of reward and risk prediction errors, providing insights into the fascinating world of decision-making.
Unraveling Reward and Risk: Insights from Caltech's Research
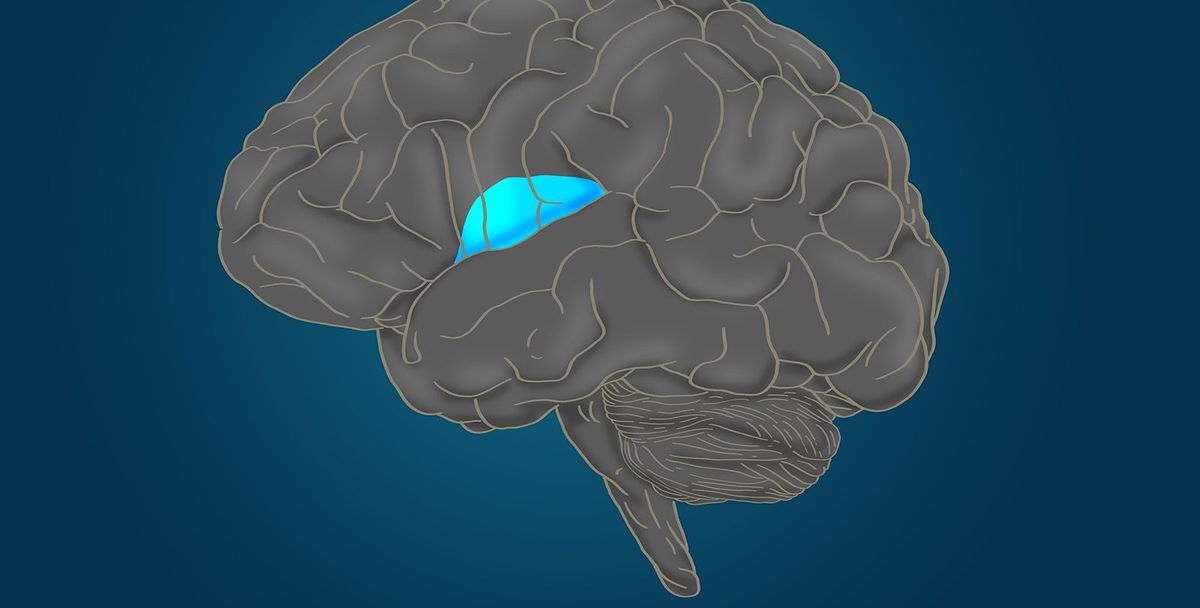
Caltech's John O'Doherty and his team have conducted groundbreaking research on how the brain represents reward and risk. By using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and implanted electrodes in patients undergoing epilepsy evaluations, they have gained valuable insights into the neural processes underlying decision-making.
Through their research, they have identified the activation of the anterior insula, a brain region involved in assessing risk and uncertainty. This finding provides a more precise understanding of how the brain evaluates potential gains and losses.
The Two-Step Process: Reward Prediction Error (RePE)
When we make decisions, our brains first calculate the reward prediction error (RePE). This involves comparing the expected value with the observed value. For example, when playing a card game, our brains assess the potential reward immediately after seeing the first card.
Jessica Williams, with her engaging and relatable voice, compares this process to a financial investment. Just like an investor calculates the potential return on investment, our brains calculate the potential reward based on the available information.
By understanding the RePE process, researchers can develop more accurate models of decision-making and learning, leading to advancements in fields such as problem gambling, addiction, and psychiatric disorders.
The Two-Step Process: Risk Prediction Error (RiPE)
Following the reward prediction error, our brains then evaluate the risk prediction error (RiPE). This process compares the expected uncertainty with the actual uncertainty, providing insights into the riskiness of the situation.
Jessica Williams, with her witty and knowledgeable personality, likens this process to a game of chance. Just like a gambler assesses the risk of a bet, our brains assess the riskiness of a decision based on the available information.
Understanding the RiPE process can help researchers gain insights into conditions such as problem gambling and addiction, and potentially develop interventions to address these psychiatric disorders.
Implications for Decision-Making and Future Research
The findings from Caltech's research have significant implications for understanding the brain's decision-making process. By unraveling how the brain processes reward and risk, researchers can develop more accurate models of decision-making and learning.
Jessica Williams, with her informative and conversational tone, highlights the potential applications of this research. Understanding the brain's decision-making process can help address psychiatric disorders such as problem gambling and addiction, leading to better interventions and treatment options.
As future research builds upon these findings, we can expect further advancements in our understanding of decision-making and its impact on our lives.