Scientists have successfully generated functional human brain tissue using a 3D printer, marking a groundbreaking achievement. The printed brain tissue consists of nerve cells and supporting cells that form networks, similar to a real human brain. This advancement allows for more accurate models of the human brain and provides a valuable tool for testing new drug candidates for brain disorders.
Groundbreaking Achievement: Functional Human Brain Tissue Created Using 3D Printer
Scientists have achieved a remarkable feat by successfully creating functional human brain tissue using a 3D printer. This groundbreaking achievement marks the first time that such complex tissue has been generated in this manner.
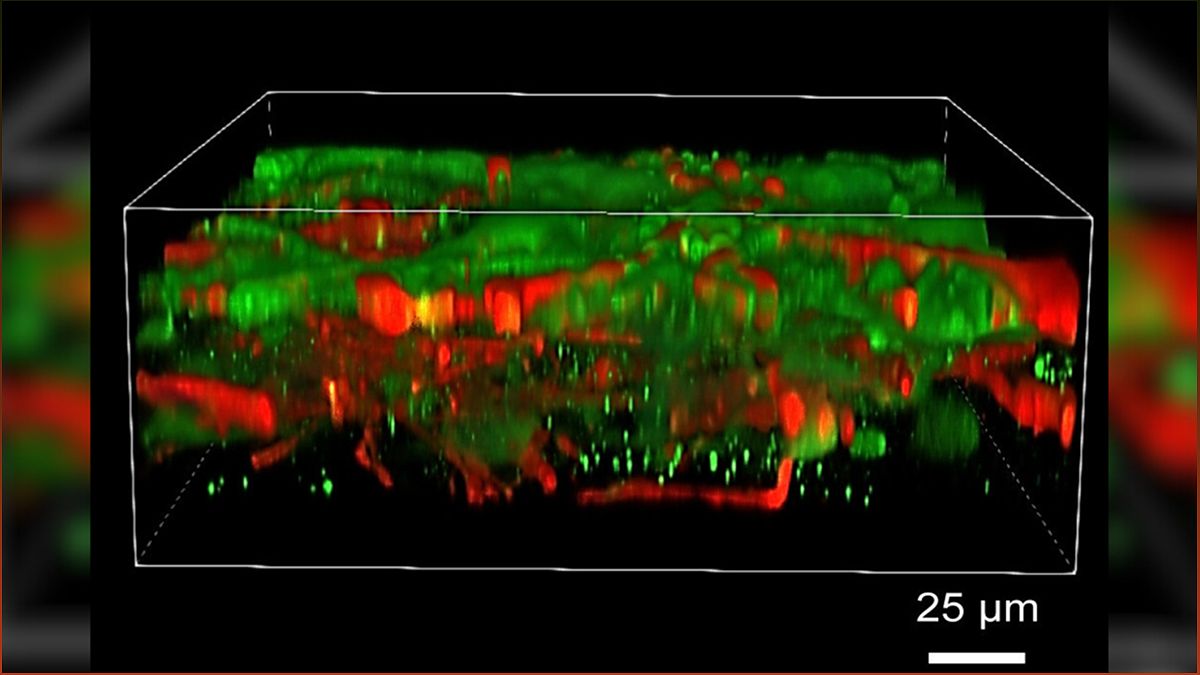
The printed brain tissue, less than 0.01 inch (0.02 centimeters) thick, consists of nerve cells and supporting cells called glia. These cells can communicate with each other and form networks, just like in a real human brain.
To create this tissue, scientists used a biological 'printer' to produce layers of gel containing stem cells. These stem cells were then stimulated with specific chemicals to develop into brain cells. The layers of tissue were carefully stacked on a lab dish to form a complete tissue model.
Advancing Brain Research: 3D-Printed Brain Tissue as a Valuable Tool
This breakthrough in creating functional brain tissue using 3D printing opens up exciting possibilities for further understanding the human brain and developing new treatments for brain disorders. The ability to create accurate models of the human brain using 3D printing offers promising avenues for future research and medical advancements.
Unlike traditional animal models, the 3D-printed brain tissue provides a more accurate representation of the unique features of the human brain. It allows scientists to have greater control over the placement of different cell types within the tissue, enabling more targeted research.
The speed and control of the 3D-printing technique make it a valuable tool for testing new drug candidates for diseases that affect brain function. Different versions of the tissue can be created to display the characteristics of specific disorders, facilitating more effective drug development.
Overcoming Challenges: The Key to Successful 3D-Printed Brain Tissue
Previous attempts to print human brain tissue fell short because the neurons and glia within the tissue were unable to form proper working connections. However, the new printing approach overcame this challenge by using a gel that was both soft enough to facilitate cell connections and strong enough to hold the layers of brain tissue together.
Unlike traditional 3D-printing methods that stack layers vertically, the researchers stacked their gel horizontally. This allowed for thinner layers, ensuring that the cells within them received ample oxygen and nutrients.
The printed stem cells successfully developed into mature neurons and glia, forming networks that resemble those found in the human brain. The cells also communicated with each other through neurotransmitters, chemical messengers commonly used in brain communication. Furthermore, cells from different regions of the brain formed connections with one another, mimicking the complex connectivity of the human brain.
Future Directions: Refining 3D Printing Technology for Greater Potential
While the 3D-printed brain tissue has its limitations, such as the inability to print multiple layers at once and the restricted overall size of the tissue, researchers are actively working to address these challenges and refine the technology.
By further improving the printing process, scientists aim to enhance the accuracy and complexity of the printed brain tissue. This will enable more comprehensive research into brain disorders and the development of personalized treatments.
This groundbreaking achievement in creating functional human brain tissue using a 3D printer opens up new horizons in neuroscience. It paves the way for exciting advancements in our understanding of the human brain and offers hope for improved treatments for brain disorders in the future.