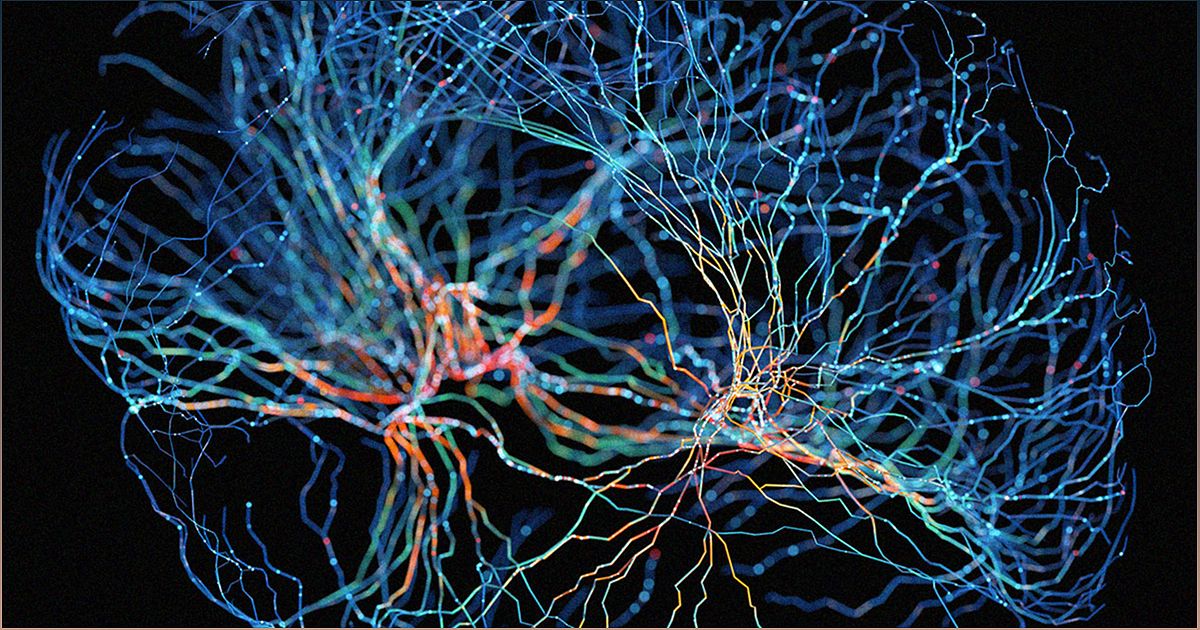
Scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have successfully created functional human brain tissue using 3D printing, opening up possibilities for treating neurological disorders like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
Breakthrough in 3D Printing: Functional Human Brain Tissue Achieved
Scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have achieved a significant milestone in the field of 3D printing by successfully creating functional human brain tissue. This groundbreaking achievement could potentially pave the way for the development of treatments for various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
In a recently published paper in the journal Cell Stem Cell, the research team described their unique approach to 3D printing brain tissue. Rather than using the traditional vertical layering method, they opted for horizontal layers of brain cells embedded in a soft "bio-ink" gel. This innovative technique allowed the neurons to grow into each other and establish connections, mimicking the structure of the human brain.
By utilizing pluripotent stem cells, the researchers ensured that each neuron had access to sufficient oxygen and nutrients from the growth media. As a result, the cells began forming networks and communicating with each other through neurotransmitters. Even when different cells from different regions of the brain were printed, they still exhibited the ability to interact in a specific and specialized manner.
Versatile and Customizable 3D-Printed Brain Tissue
The advantage of this 3D-printed brain tissue over existing "mini-brain" models, known as organoids, lies in its versatility. The researchers can produce various types of neurons and assemble them in any desired configuration. This flexibility allows for a more comprehensive study of how cells communicate with each other under different conditions, particularly in tissue affected by diseases like Alzheimer's.
Furthermore, this technology could potentially be used for drug evaluation purposes. By printing specific brain tissue, researchers can examine how different compounds and treatments affect the communication between nerve cells. This approach provides a more holistic understanding of the complex networks within the brain.
One notable aspect of this achievement is that the research team used a commercially available bioprinter. This accessibility means that other institutions and researchers can also utilize this technology to print their own human brain tissue, expanding the scope of this groundbreaking research.
Future Directions and Advancements
Looking ahead, the team is now focused on refining their printing technique to enable the printing of cells in predefined orientations. This development would provide even greater control over the types of brain tissue that can be manufactured.
In summary, the successful 3D printing of functional human brain tissue by scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison represents a significant advancement in the field of neuroscience. This technology has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of stem cell biology, neuroscience, and the underlying mechanisms of various neurological and psychiatric disorders. With further research and development, this approach could lead to groundbreaking treatments and therapies for individuals suffering from these conditions.